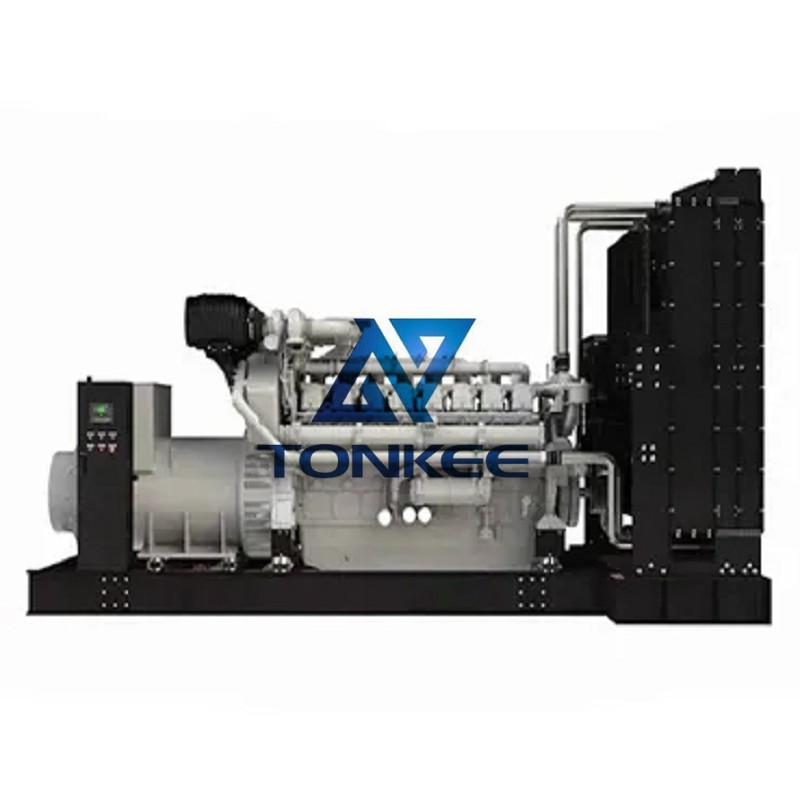
Power Output: The power output of a diesel engine is measured in kilowatts (kW) or horsepower (HP).
It represents the amount of electrical power the engine can generate. Diesel gensets are available in a wide range of power outputs, from a few kilowatts for small residential applications to several megawatts for large-scale industrial use.
Displacement: The displacement of a diesel engine refers to the total volume of all the cylinders in the engine. It is usually measured in liters (L) or cubic centimeters (cc). The displacement affects the engine's torque and power characteristics. Larger displacement engines generally offer more power and torque.
Compression Ratio: The compression ratio of a diesel engine is the ratio of the volume of the combustion chamber at the bottom of the piston's stroke to the volume at the top of the stroke. It determines the engine's thermal efficiency and power output. Higher compression ratios result in more efficient combustion and increased power output.
Cooling System: Diesel engines in gensets require an efficient cooling system to prevent overheating. The cooling system typically consists of a radiator, coolant, water pump, and a fan. The cooling system helps maintain the engine's operating temperature within acceptable limits, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Fuel System: Diesel engines utilize a fuel injection system to deliver fuel into the combustion chamber. Common fuel injection systems include direct injection and indirect injection. The fuel system must ensure efficient and reliable delivery of fuel, as diesel fuel is less volatile than gasoline and requires higher compression for combustion.
Governor: The governor is a device that controls the engine speed and maintains it at a constant level, even under varying load conditions. It regulates the amount of fuel delivered to the engine based on the electrical load demand. A well-functioning governor is essential for stable and reliable power output from the diesel genset.
Emission Standards: Diesel engines produce exhaust emissions that need to comply with environmental regulations.
The emission standards dictate the acceptable levels of pollutants emitted by the engine, such as nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and carbon monoxide (CO). Modern diesel gensets are equipped with emission control technologies to minimize their environmental impact.
Noise Level: Diesel gensets can be noisy due to the combustion process and mechanical components. Noise levels are measured in decibels (dB). Lower noise levels are desirable, especially in residential or noise-sensitive areas. Many gensets are equipped with soundproof enclosures or noise reduction measures to minimize the noise generated during operation.




